The Importance of Securing IoT Pacemakers to Increase Patient Safety
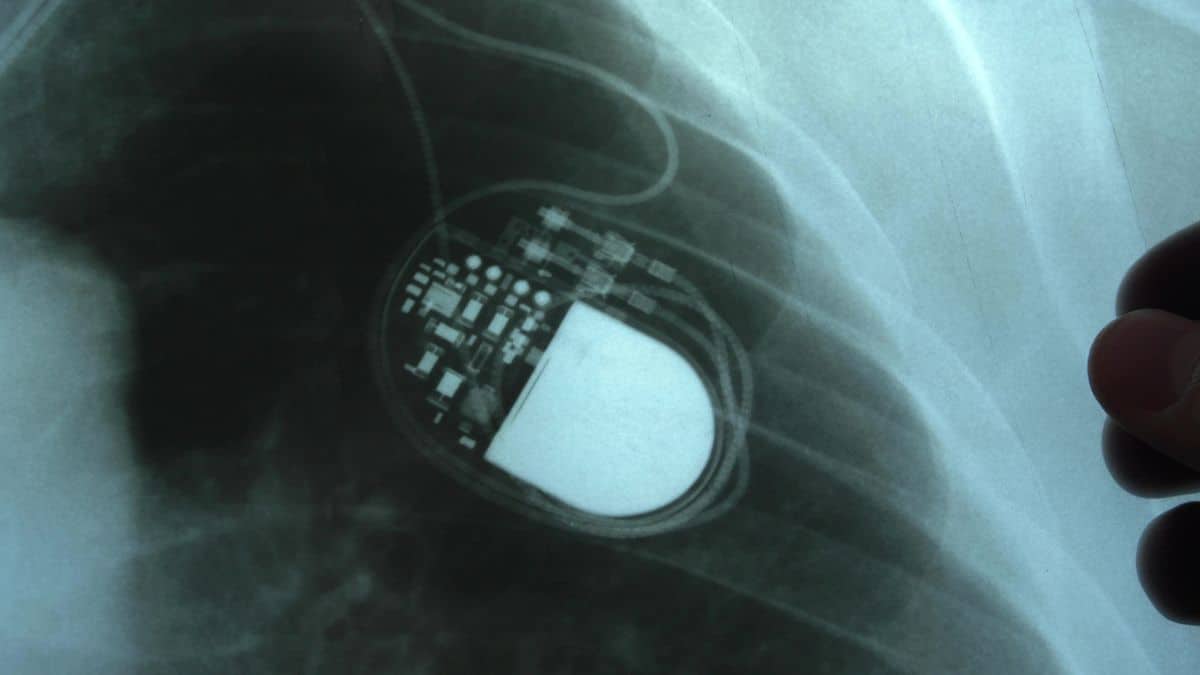
Pacemakers are life-saving devices that regulate the heart rhythm of patients with cardiac conditions. Connected pacemakers leverage internet connectivity and smart technology to further enhance patient care. Wireless connectivity allows the device to send data to healthcare providers in real time, and some connected pacemakers even offer apps that patients can use to communicate directly with doctors, reducing the need for in-office visits.
Overall, Internet of Things (IoT) pacemakers enhance patient safety, improve their quality of life, and deliver more personalized and efficient care. Despite the benefits, IoT pacemakers can also introduce cybersecurity risks and, in turn, health risks.
IoT Pacemaker Vulnerabilities Pose Risk to Patients
Researchers have long been concerned about the security of IoT pacemakers. In 2008, the Medical Device Security Center hacked a pacemaker to prove malicious actors could leverage connectivity to gain access to the device and alter or disrupt functionality. While threat actors can use a variety of cyberattacks to compromise IoT devices, they can also leverage unpatched, critical vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access.
There have already been several notable critical vulnerabilities that directly impacted IoT pacemakers:
- August 2017: Security researchers identified a critical vulnerability in several Abbott Laboratories’ pacemakers. The vulnerability impacted the transmitter used by the pacemaker to send information. Once a threat actor had access to the transmitter, they could issue commands, change settings, or alter the device’s functionality. The Federal Drug Administration (FDA) also issued a recall of 465,000 Abbott devices.
- March 2019: Two critical vulnerabilities were discovered in the Conexus telemetry protocol used by Medtronic MyCarelink monitors. The vulnerabilities allowed a threat actor to alter the functionality of implanted cardiac devices.
- February 2021: Dr. Marie Moe published five years’ worth of research from the Pacemaker Hacking Project, which focused on five critical vulnerabilities impacting BIOTRONIK pacemakers.
- July 2023: The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued an advisory regarding a breach of Medtronic’s Paceart Optima System, which compiles and manages cardiac device data. If exploited, the vulnerability allowed a threat actor to delete, steal, or modify data from a cardiac device.
Patient safety could be severely compromised if a pacemaker’s functionality is altered or otherwise compromised. As such, efforts have been made to address the risk associated with vulnerabilities and improve cybersecurity safeguards for pacemakers.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for IoT Pacemakers
In 2024, the FDA issued updated guidance for manufacturers emphasizing the need for robust security measures in IoT medical devices. The FDA recommends several measures to enhance the cybersecurity of medical devices, including pre-market security assessments, where manufacturers conduct risk assessments during development, and post-market surveillance of cybersecurity incidents and vulnerabilities.
In addition to the role manufacturers play in improving the security of IoT pacemakers, there are actionable steps that patients and healthcare providers can take.
Patient and Provider Education
To date, there have been no documented cases of cyber attacks against pacemakers impacting patient health. However, the risk is real. Both patients who rely on IoT pacemakers and their healthcare providers should be aware of potential cybersecurity risks and best practices to mitigate these risks.
Strong Authentication
Healthcare networks are often easy targets for threat actors. To make their networks more secure, healthcare organizations can leverage robust authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized personnel can access or modify the pacemaker’s settings.
Update Firmware
IoT pacemakers occasionally require firmware updates or patches. As with any software updates, firmware updates can cause devices to malfunction, although the risk is low. Patients should engage with their healthcare provider to perform all necessary updates alongside industry technicians.
Because many IoT pacemakers utilize apps for communication, patients should ensure that both the app and their mobile devices are regularly updated.
Remediate Vulnerabilities
In addition to firmware updates, patients and physicians should be aware of the ongoing risk of critical vulnerabilities.
Healthcare facilities can utilize passive scanning technology to identify vulnerable IoT medical devices connected to their network. Passive-first approaches to scanning can provide several valuable insights about the vulnerabilities that attackers are most likely to exploit, including:
- Exploitable vulnerabilities within the environment
- Exploitable vulnerabilities for each specific device
- Provide guidance for patching based on exploitability
- Mitigation recommendations specific to the device, such as applying security updates or using compensating controls for medical imaging equipment
Monitor for Anomalous Behavior
All devices on a network should only communicate with known IP addresses in well-understood ways. Early detection of anomalous behavior can enhance a security team’s ability to respond to an in-progress attack. IoT pacemakers should only communicate with known, approved devices and networks and only be accessed by authorized personnel.
Enhance Detection and Investigation
Cyber attacks can originate from anywhere within a network, and threat actors commonly target vulnerable devices to gain access and move laterally within the broader network. Incorporating IoT devices, including pacemakers, into security monitoring tools can enhance attack detection and investigation for healthcare organizations.
When security teams receive high-fidelity alerts that cover the totality of a network, they can detect attacks faster and make better decisions, potentially mitigating the severity of a cyberattack.
When organizations employ solutions that can capture network packet data, security analysts obtain important forensic data needed to determine root cause such as:
- RAM from servers (important for fileless malware, which doesn’t touch magnetic media)
- Traffic information from network devices
- Data transferred to an FTP server
How Asimily Helps Defend Connected Pacemakers
Asimily is designed with IoT devices in mind, monitoring network traffic to and from IoT devices, such as pacemakers, and sending alerts based on anomalous behavior that might indicate an attack.
Our risk scoring provides information on high-risk vulnerabilities, while our proprietary algorithm leverages vast amounts of data from resources like EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System), Software Bills of Material (SBOMs), Common Vulnerability and Exposure (CVE) lists, the MITRE ATT&CK Framework, and NIST Guidelines. It understands your unique environment, so our deep contextual recommendation engine can provide the most efficient actionable remediation steps to reduce risk and save time.
Asimily’s recommendations can easily be applied in several ways, including through seamless integration with NACs, firewalls, or other network enforcement solutions.
To learn more about Asimily, download our whitepaper, IoT Device Security in 2024: The High Cost of Doing Nothing, or contact us today.
Secure Every IoT Device.
Automatically.
Cyber threats move fast — so should you. Asimily gives instant inventory and smart, prioritized risk mitigation insights for every IoT, OT, and IoMT device — so you can take action before threats strike.